Quick Tip: Endless scrolling with SpriteKit and SWIFT (Part 1 of 2)
Endless scrolling with background tiles
Welcome to my tutorial series about scrolling:
This video gives an impression what I’ll show today:
1. About the algorithm and the background tiles
Creating the image tiles for the scrolling parts of the background:
First we need a background image:

Let’s mirror this image and add the new one at the right side:

Copy the original image and append it at the right side. In our app we will have three sprite nodes, one for each image tile:

Scrolling will start at the left side:

Let’s add a static background image:

To scroll right, move the background tiles in the left direction:

If the end at the right side is reached:

Move the background tiles back to the start position:

The SpriteKits object hierarchy will be created this way:
- scene (SKScene)
- backgroundNode (SKSpriteNode)
- worldNode (SKNode)
- leftTileNode (SKSpriteNode)
- middleTileNode (SKSpriteNode)
- rightTileNode (SKSpriteNode)
- spriteNode (SKSpriteNode)
The worldNode will be moved to implement the scrolling.
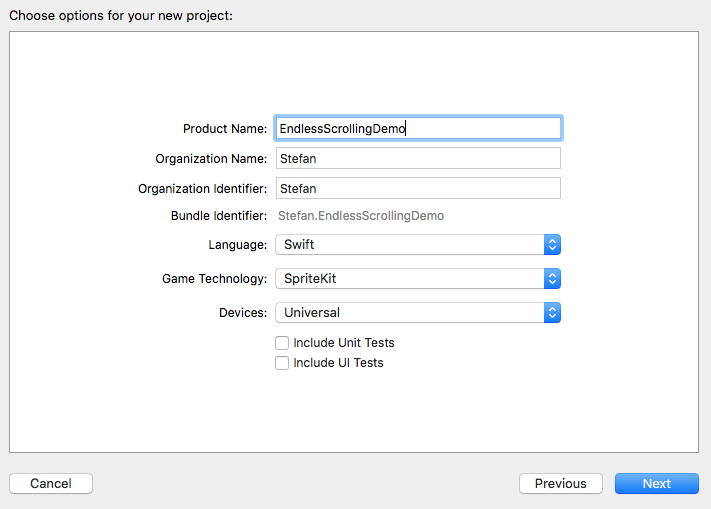
2. Create the SWIFT project:
Create a new Sprite Kit project:
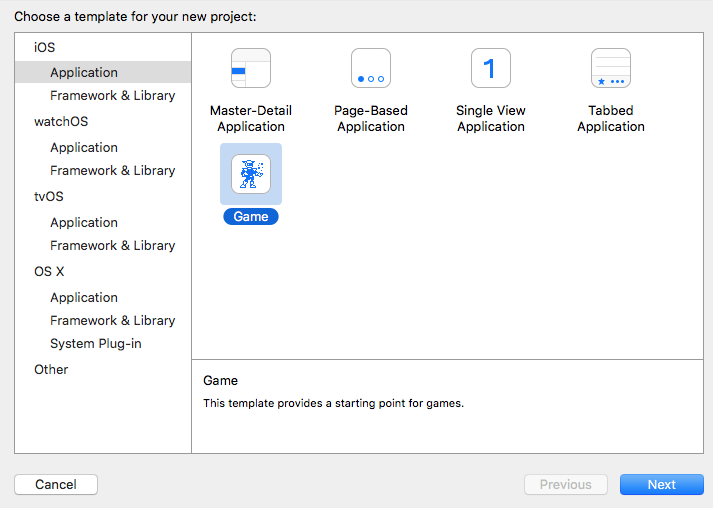
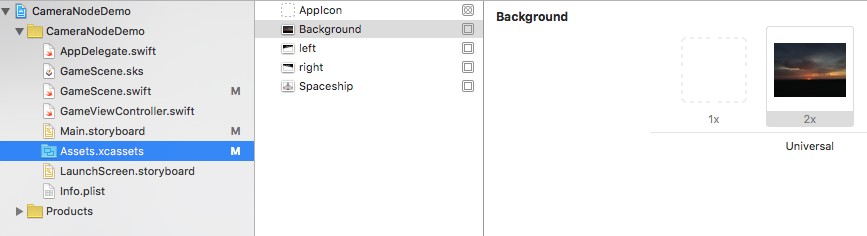
Open Asset Catalogue and add three images (Background, LeftTile, rightTile)
Open GameScene.swift:
Replace the complete code with this snippet:
(For explanation check the comments inside the code snippet)
//
// GameScene.swift
// EndlessScrollingDemo
//
// Created by STEFAN on 13/11/15.
// Copyright (c) 2015 Stefan. All rights reserved.
//
import SpriteKit
class GameScene: SKScene {
// Declare the globaly needed sprite kit nodes
var worldNode: SKNode?
var spriteNode: SKSpriteNode?
// store the width of the NodeTiles
var nodeTileWidth: CGFloat = 0.0
// store the start position of the movement
var xOrgPosition: CGFloat = 0
override func didMoveToView(view: SKView) {
// Setup static background
let backgroundNode = SKSpriteNode(imageNamed: "Background")
backgroundNode.size = CGSize(width: self.frame.width, height: self.frame.height)
backgroundNode.anchorPoint = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
backgroundNode.zPosition = -10
self.addChild(backgroundNode)
// Setup world
worldNode = SKNode()
self.addChild(worldNode!)
// Setup dynamic background tiles
// Image of left and right node must be identical
let leftNode = SKSpriteNode(imageNamed: "LeftTile")
let middleNode = SKSpriteNode(imageNamed: "RightTile")
let rightNode = SKSpriteNode(imageNamed: "LeftTile")
nodeTileWidth = leftNode.frame.size.width
leftNode.anchorPoint = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
leftNode.position = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
middleNode.anchorPoint = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
middleNode.position = CGPoint(x: nodeTileWidth, y: 0)
rightNode.anchorPoint = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
rightNode.position = CGPoint(x: nodeTileWidth * 2, y: 0)
// Add tiles to worldNode. worldNode is used to realize the scrolling
worldNode!.addChild(leftNode)
worldNode!.addChild(rightNode)
worldNode!.addChild(middleNode)
// Setup sprite
spriteNode = SKSpriteNode(imageNamed: "Spaceship")
spriteNode?.position = CGPoint(x:CGRectGetMidX(self.frame), y:CGRectGetMidY(self.frame))
spriteNode?.xScale = 0.1
spriteNode?.yScale = 0.1
spriteNode?.zPosition = 10
self.addChild(spriteNode!)
}
// Implement the scrolling, triggered by swipe gestures
override func touchesMoved(touches: Set<UITouch>, withEvent event: UIEvent?) {
for touch in touches {
// Touch position
let xTouchPosition = touch.locationInNode(self).x
if xOrgPosition != 0.0 {
// calculate the new position
let xNewPosition = worldNode!.position.x \+ (xOrgPosition \- xTouchPosition)
// Check if right end is reached
if xNewPosition <= -(2 * nodeTileWidth) {
worldNode!.position = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0)
print("Right end reached")
// Check if left end is reached
} else if xNewPosition >= 0 {
worldNode!.position = CGPoint(x: -(2 * nodeTileWidth), y: 0)
print("Left end reached")
} else {
worldNode!.position = CGPoint(x: xNewPosition, y: 0)
}
// Rotate sprite depending on direction
if xTouchPosition < xOrgPosition {
spriteNode?.zRotation = CGFloat(M_PI/2.0)
} else {
spriteNode?.zRotation = -CGFloat(M_PI/2.0)
}
}
// Store the current touch position to calculate the delta in the next iteration
xOrgPosition = xTouchPosition
}
}
override func touchesEnded(touches: Set<UITouch>, withEvent event: UIEvent?) {
// Reset value for the next swipe gesture
xOrgPosition = 0
}
override func update(currentTime: CFTimeInterval) {
/* Called before each frame is rendered */
}
}
You can download the complete sample from my Github repository.
I’ll show an improved version with a smoother scrolling in part 2. You can support me by downloading my Apps from the Apple AppStore:
That’s all for today.
Cheers,
Stefan
